sấy phun: Các loại, Những lợi ích, và Ứng dụng
Sấy phun là một quy trình công nghiệp được sử dụng để chuyển đổi vật liệu lỏng thành bột hoặc hạt chỉ trong một bước. Điều này liên quan đến việc nguyên tử hóa chất lỏng thành những giọt nhỏ và làm khô chúng nhanh chóng trong luồng không khí nóng., tạo thành dạng bột dễ vận chuyển và đóng gói. Do tính hiệu quả của nó, tính linh hoạt, và khả năng duy trì chất lượng sản phẩm ổn định, sấy phun được sử dụng rộng rãi trong các ngành công nghiệp như thực phẩm, dược phẩm, và hóa chất.
Hãy bắt đầu với lịch sử ngắn gọn về sấy phun!
Lịch sử sấy phun
Sấy phun được áp dụng lần đầu tiên vào thế kỷ 19 bởi một kỹ sư người Pháp, người đã phát triển phương pháp sấy men rượu.. Quá trình này được sử dụng rộng rãi vào giữa thế kỷ 20 khi máy sấy phun công nghiệp đầu tiên được giới thiệu.. Ban đầu, máy phun vòi phun đã được sử dụng, nhưng máy phun quay sau đó đã được phát triển để nâng cao hiệu quả. Kể từ đó, công nghệ đã phát triển để đáp ứng nhiều ứng dụng công nghiệp.

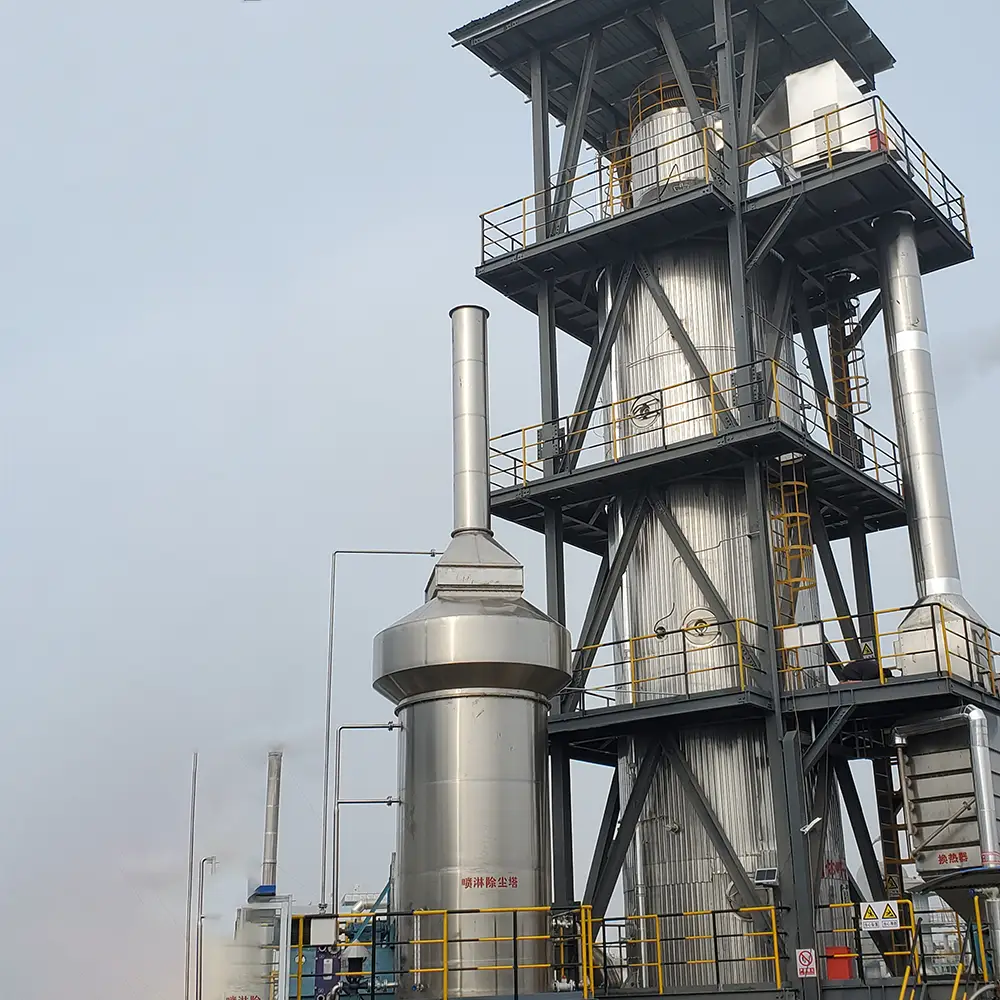
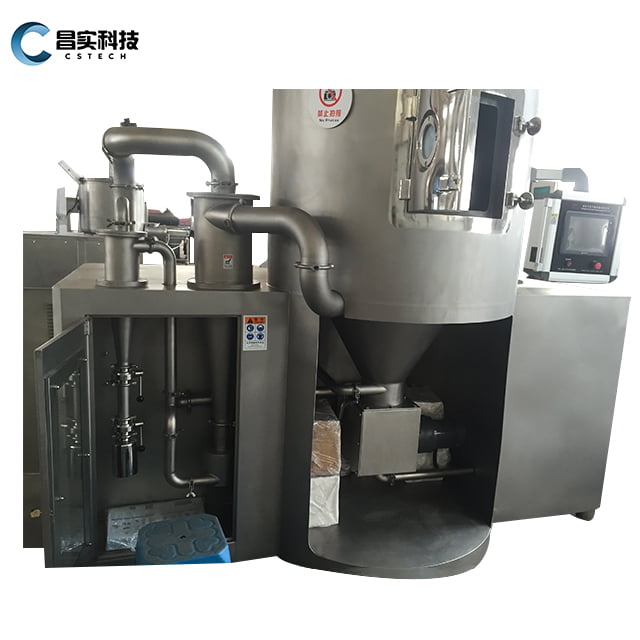
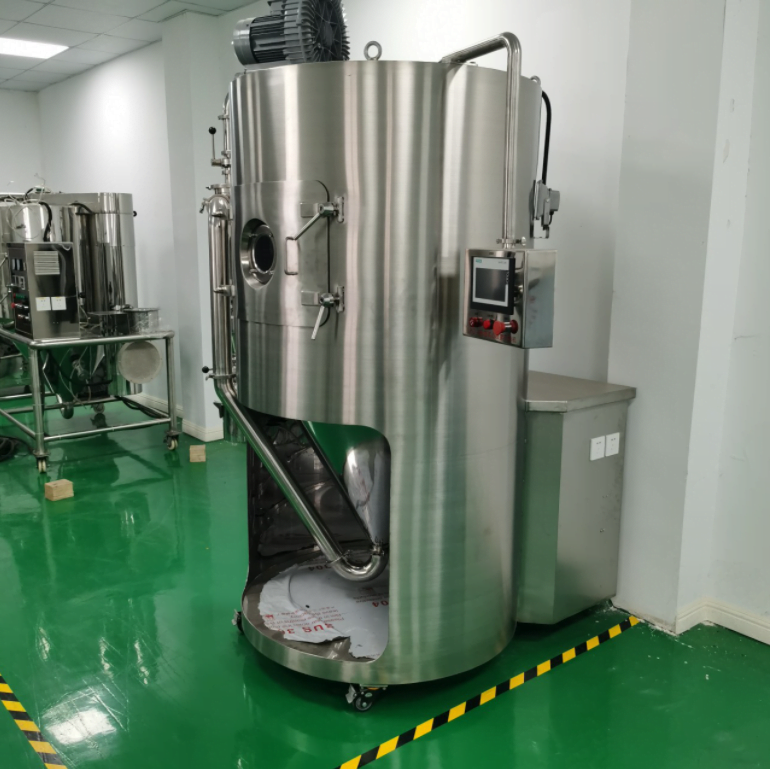
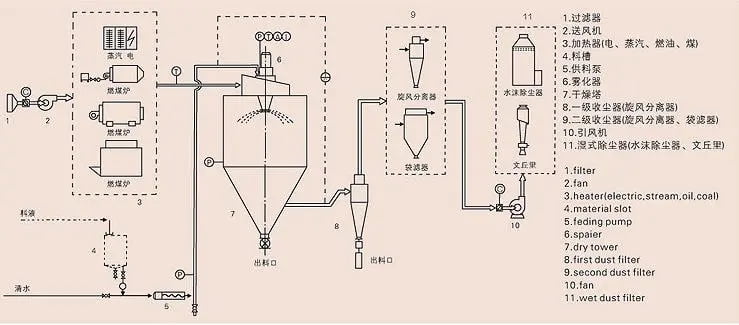
Máy sấy phun hoạt động như thế nào
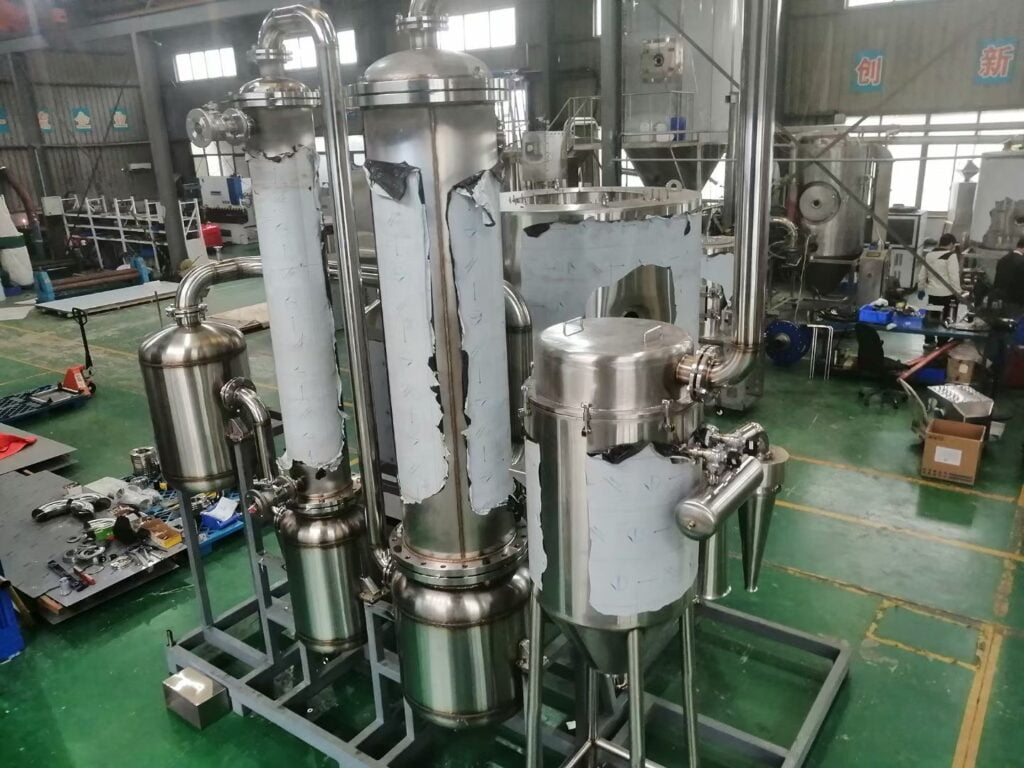
Hệ thống sấy phun điển hình bao gồm:
- Chuẩn bị thức ăn: Thành phần được trộn lẫn, độ nhớt được điều chỉnh, và hỗn hợp được đồng nhất để tạo ra thức ăn lỏng.
- Nguyên tử hóa: Chất lỏng được bơm vào vòi phun hoặc đĩa quay, phá vỡ nó thành những giọt nhỏ.
- Sấy khô: Các giọt được làm khô trong buồng bằng luồng không khí nóng, với các thông số như nhiệt độ và luồng không khí được kiểm soát cẩn thận để đạt được kích thước hạt và độ ẩm mong muốn.
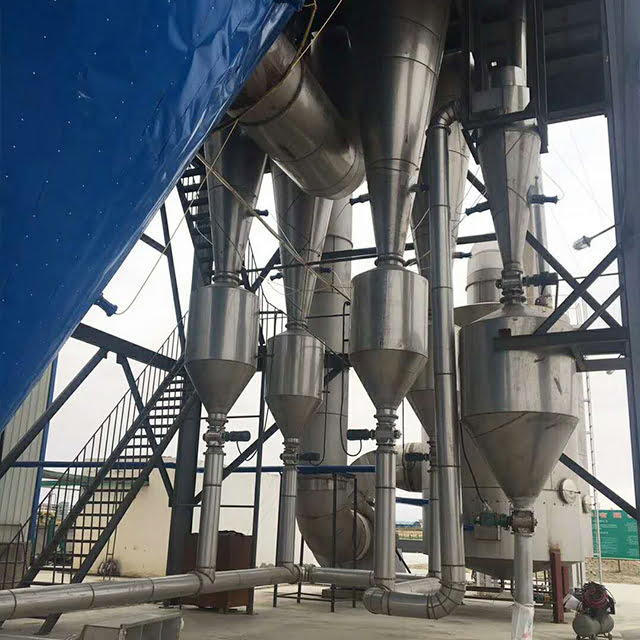
- Bộ sưu tập: Bột khô được thu thập bằng các hệ thống như lốc xoáy hoặc túi lọc để đóng gói hoặc xử lý tiếp.
Sự bay hơi nhanh chóng của các giọt chất lỏng trong không khí nóng là mấu chốt của quá trình sấy phun. Tốc độ sấy bị ảnh hưởng bởi kích thước giọt, nhiệt độ, vận tốc không khí, và độ ẩm của sản phẩm.
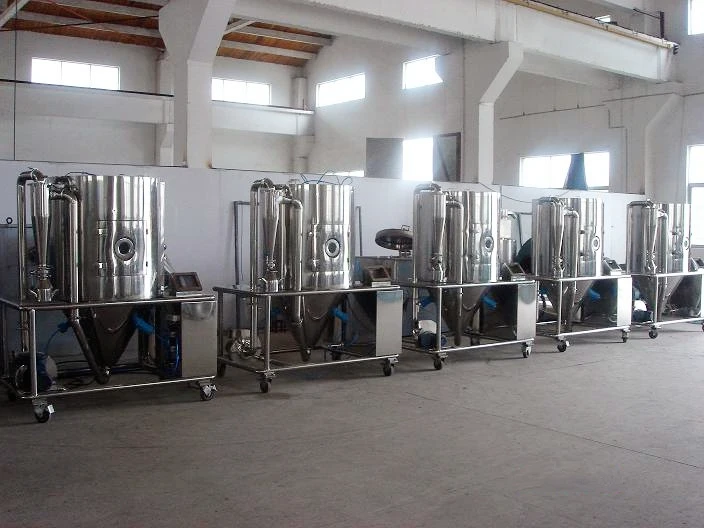
Các loại máy sấy phun
Có một số loại máy sấy phun, mỗi thiết kế cho các ứng dụng cụ thể:
- Máy phun quay hoặc ly tâm: Sử dụng bánh xe quay để nguyên tử hóa chất lỏng thành giọt, thích hợp cho thức ăn có độ nhớt cao và nhiều loại vật liệu.
- Máy phun áp lực: Sử dụng máy bơm cao áp để tạo ra sự đồng nhất, bột đồng nhất với sự phân bố kích thước hạt hẹp, thường được sử dụng trong ngành công nghiệp thực phẩm và sữa.
- Máy phun hai chất lỏng: Sử dụng khí nén (chẳng hạn như không khí hoặc hơi nước) nguyên tử hóa chất lỏng, thường được sử dụng trong các ứng dụng quy mô thí điểm.
- Hệ thống kết hợp: Kết hợp sấy phun với tầng sôi để nâng cao hiệu quả và đặc tính sản phẩm, đặc biệt để sản xuất vật liệu kết tụ.
- Hệ thống chu trình khép kín: Được thiết kế cho các sản phẩm nhạy cảm hoặc dung môi hữu cơ, sử dụng nitơ thay vì không khí để ngăn chặn quá trình oxy hóa và tăng cường an toàn.
Ưu điểm của sấy phun
- Xử lý một bước: Chuyển đổi chất lỏng trực tiếp thành bột chỉ trong một bước, làm cho nó trở thành một lựa chọn hiệu quả về mặt chi phí cho sản xuất quy mô nhỏ hoặc sản xuất thí điểm.
- Tính linh hoạt: Thích hợp cho nhiều loại vật liệu, từ thực phẩm và dược phẩm đến hóa chất và mỹ phẩm.
- Chất lượng sản phẩm nhất quán: Tạo ra các hạt đồng nhất ổn định và dễ xử lý, với đặc tính dòng chảy tốt.
- Bảo quản hoạt chất: Duy trì hiệu lực và hiệu quả của các hợp chất hoạt động, lý tưởng cho dược phẩm và dược phẩm sinh học.
- Giảm chất gây ô nhiễm: Giảm thiểu ô nhiễm vi sinh vật, đặc biệt quan trọng trong các ứng dụng thực phẩm và dược phẩm.
Ứng dụng công nghiệp của sấy phun
Sấy phun được sử dụng trong nhiều ngành công nghiệp khác nhau, chẳng hạn như:
- Đồ ăn: Để tạo ra các sản phẩm hòa tan như cà phê, sữa bột, và hương liệu, trong khi vẫn giữ được hương vị, hương thơm, và màu sắc.
- Dược phẩm: Dùng để sản xuất bột, hạt, và máy tính bảng, cũng như đóng gói các hoạt chất.
- Hóa chất: Để làm khô dung môi và tạo ra các sản phẩm như chất xúc tác và chất màu.
- nông nghiệp: Để sản xuất thức ăn chăn nuôi, phân bón, và thuốc trừ sâu.
- Công nghệ sinh học: Để sản xuất protein tái tổ hợp, vắc-xin, và các dược phẩm sinh học khác.
- Môi trường: Để xử lý nước thải, chất thải rắn, và các chất gây ô nhiễm không khí.
- Mỹ phẩm: Để tạo bột và các sản phẩm chăm sóc cá nhân.
- Vật liệu pin: Ứng dụng mới nổi trong sản xuất vật liệu cực âm và cực dương cho pin lithium-ion.
Nhược điểm của sấy phun
Mặc dù lợi ích của nó, sấy phun có một số nhược điểm:
- Độ nhớt thức ăn hạn chế: Thường xử lý các nguồn cấp dữ liệu có độ nhớt dưới đây 500 rết, có thể cần pha loãng.
- Chi phí vốn cao: Đắt tiền để mua và vận hành, với mức tiêu thụ năng lượng cao.
- Năng lượng chuyên sâu: Cần năng lượng đáng kể để làm nóng không khí và phun nguyên liệu.
- Mối quan ngại về an toàn hoạt động: Bột khô có thể dễ cháy hoặc nổ, yêu cầu các biện pháp an toàn mạnh mẽ.
Giúp việc sấy phun mang lại hiệu quả cho doanh nghiệp của bạn
Để tối ưu hóa tỷ lệ chi phí-lợi ích của sấy phun, điều quan trọng là phải chọn đúng thiết bị và nhà cung cấp. Những đổi mới gần đây, chẳng hạn như máy phun nguyên tử quay tốc độ cao với công nghệ mang từ tính, mang lại hiệu quả cao hơn và giảm chi phí bảo trì, làm cho sấy phun trở thành một lựa chọn khả thi hơn cho nhiều ứng dụng.
Phần kết luận
Sấy phun đã trở thành một phương pháp chủ yếu trong nhiều ngành công nghiệp nhờ những ưu điểm của nó so với các kỹ thuật sấy khác.. Mặc dù nó có độ phức tạp và đòi hỏi chuyên môn kỹ thuật, lợi ích thường lớn hơn những hạn chế. Phân tích kỹ lưỡng về ưu điểm và nhược điểm của nó có thể giúp xác định xem nó có phù hợp với nhu cầu cụ thể của bạn hay không.
Câu hỏi thường gặp
- Các lựa chọn thay thế cho sấy phun? Các lựa chọn thay thế như máy sấy vòng hoặc máy sấy flash roto có thể phù hợp cho một số ứng dụng nhất định.
- Nhiệt độ trong sấy phun? Tiêu biểu, không khí được làm nóng đến 200°C (khoảng 400°F) được sử dụng để làm khô chất lỏng nguyên tử.
- Phun sấy vs. Sấy đông lạnh? Sấy phun thường hiệu quả hơn đối với một số ứng dụng nhất định, như được chứng minh bằng các nghiên cứu về độ hòa tan và độ ẩm.
- Sản phẩm không phù hợp để sấy phun? Sản phẩm có độ nhớt cao, nhạy cảm với nhiệt, hoặc phản ứng có thể không lý tưởng cho việc sấy phun.










