Nguyên lý cơ bản của sự hóa lỏng
Sự hóa lỏng xảy ra khi bạn cho một chất khí hoặc chất lỏng đi lên qua các hạt rắn mịn với tốc độ khiến chúng hành xử như một chất lỏng.
Nguyên lý cơ bản liên quan đến lực hướng lên từ chất lỏng làm cân bằng trọng lượng của các hạt, khiến chúng nâng lên và trộn lẫn nhanh chóng.
Bạn thấy trạng thái hóa lỏng khi lớp chất rắn giãn nở và dạng bong bóng, giống như nước sôi.
Nguyên lý hóa lỏng cho phép bạn đạt được sự pha trộn tuyệt vời, truyền nhiệt, và phản ứng hóa học.
Nhiều ngành công nghiệp phụ thuộc vào quá trình này để hoạt động hiệu quả.
Bài học chính
Sự hóa lỏng xảy ra khi chất khí hoặc chất lỏng di chuyển lên trên qua các hạt rắn, làm cho chúng hoạt động giống như một chất lỏng. Quá trình này tăng cường trộn và truyền nhiệt.
Hiểu các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến quá trình hóa lỏng, chẳng hạn như kích thước hạt và mật độ, giúp nâng cao hiệu quả trong các ứng dụng công nghiệp.
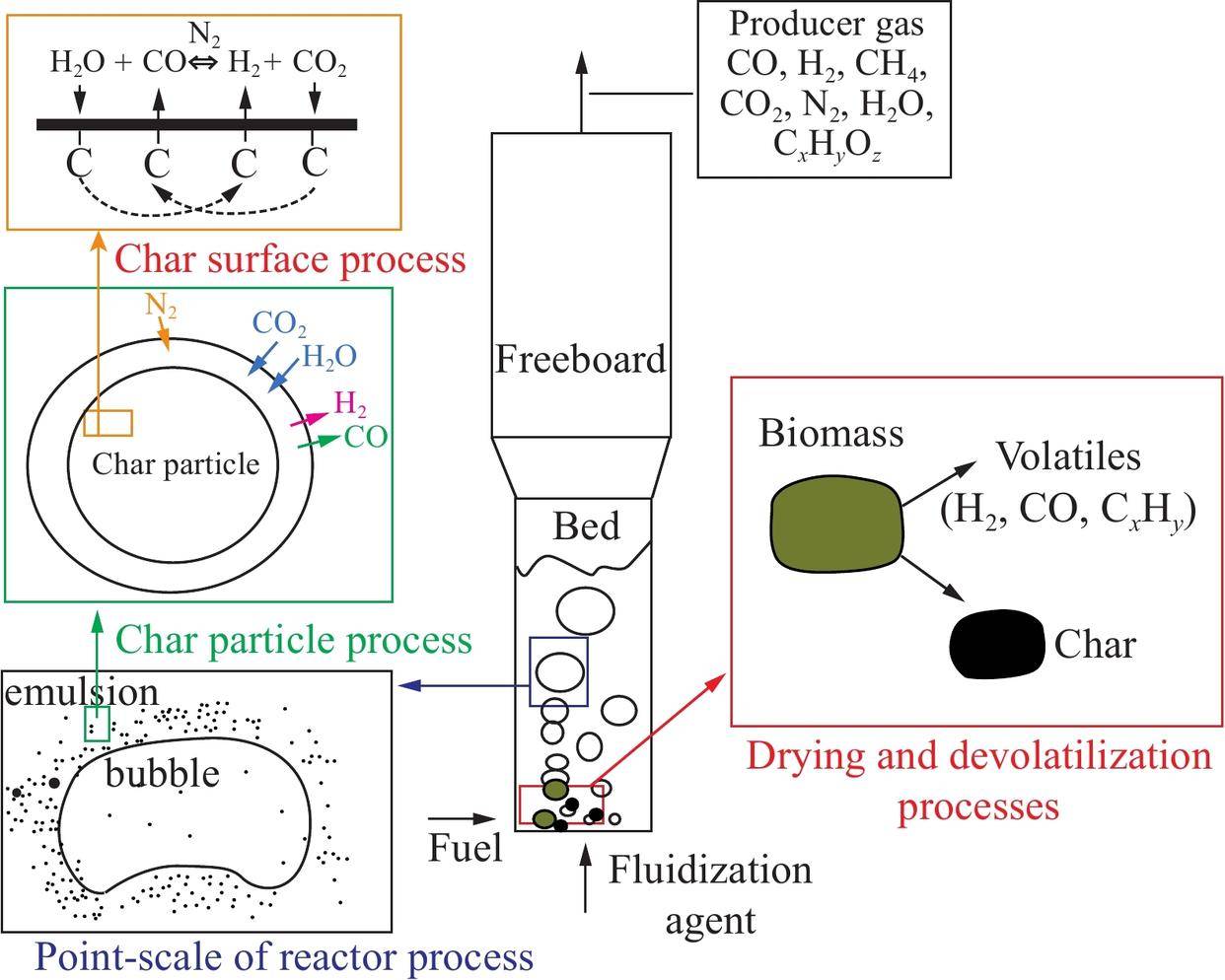
Lò phản ứng tầng sôi được sử dụng rộng rãi trong các ngành công nghiệp như sản xuất hóa chất và sản xuất năng lượng nhờ khả năng trộn chất rắn và chất lỏng một cách hiệu quả..
Sử dụng tầng sôi mang lại lợi thế hơn các phương pháp truyền thống, bao gồm kiểm soát độ ẩm tốt hơn và thời gian khô nhanh hơn cho các vật liệu khác nhau.
Giám sát nhiệt độ và luồng không khí là rất quan trọng để vận hành an toàn và hiệu quả tầng sôi, đảm bảo hiệu suất tối ưu.
Nguyên tắc cơ bản
Giải thích về chất lỏng
Bạn có thể hiểu nguyên lý cơ bản của quá trình hóa lỏng bằng cách xem các hạt rắn mịn hoạt động như thế nào khi bạn truyền chất khí hoặc chất lỏng qua chúng. Nguyên tắc cơ bản bắt đầu với việc chất lỏng di chuyển lên trên. Chuyển động này tạo ra một lực nâng các hạt. Khi lực hướng lên phù hợp với trọng lượng của các hạt, lớp chất rắn bắt đầu giãn nở. Bạn thấy bong bóng hình thành, và các hạt trộn nhanh chóng. Chiếc giường hoạt động như một chất lỏng sôi.
Sự khởi đầu của sự mất ổn định ban đầu trong lớp hạt xảy ra trước sự khuếch tán khí ổn định trong các kẽ hở và được gây ra bởi một lực động lượng tới hạn có thể thắng quán tính của các hạt.. Lực động lượng tới hạn được cung cấp bởi vận tốc khí bề mặt tới hạn bạnc ở dạng dòng khuếch tán khối tới hạn. Người ta thấy rằng chuyển động đầu tiên của các hạt có thể được dự đoán bằng số Rayleigh nhất thời tới hạn được xác định bởi vận tốc bề mặt tới hạn bằng vận tốc hóa lỏng tối thiểu, bạnbà già. Sự khởi đầu của quá trình hóa lỏng bắt đầu được phát hiện xảy ra ở thời điểm số Rayleigh nhất thời tới hạn của 3.1, gần với giá trị lý thuyết thấp nhất cho sự đối lưu nổi trong môi trường xốp được giới hạn bởi các bề mặt tự do.
Bạn cần chú ý đến một số yếu tố quan trọng ảnh hưởng đến nguyên tắc cơ bản. Chúng bao gồm mật độ hạt, kích cỡ, hình dạng, và cách các hạt được nén lại với nhau. Cách chất lỏng di chuyển qua giường cũng có vấn đề. Bạn có thể thấy các yếu tố này phối hợp với nhau như thế nào trong bảng dưới đây:
Diện mạo | Những phát hiện |
|---|---|
Ảnh hưởng mật độ hạt | Mật độ hạt cao hơn dẫn đến hiệu suất hóa lỏng kém hơn trong giai đoạn đầu. |
Thủy động lực học | Những ảnh hưởng đáng kể đến thủy động lực học được quan sát, có lỗi trong dự đoán đối với các hạt mật độ cao. |
Giai đoạn hóa lỏng | Ba giai đoạn hóa lỏng riêng biệt được xác định, bị ảnh hưởng bởi sự phân bố kích thước hạt. |
Phân bố kích thước hạt | PSD hẹp dẫn đến khả năng chảy tốt hơn và tốc độ hóa lỏng tối thiểu thấp hơn (bạn*mf). |
Hạt nhóm C | PSD rộng hơn dẫn đến độ giãn nở của lớp cao hơn và cải thiện khả năng tiếp xúc với khí-rắn. |
Điều chế nano | Nâng cao chất lượng hóa lỏng của bột nhóm C, chỉ ra tầm quan trọng của quy mô và sự phân bố. |
Bạn có thể thấy các hành vi khác nhau trong quá trình hóa lỏng tùy thuộc vào loại hạt. Ví dụ:
Các hạt Geldart B/D dễ dàng tạo thành bong bóng, nhưng giường không mở rộng nhiều.
Các hạt Geldart A giãn nở đều, điều đó làm cho chiếc giường ổn định hơn.
Sóng xung kích và sóng liên tục di chuyển qua lớp trong quá trình dòng khí, cho thấy nguyên tắc cơ bản hoạt động như thế nào trong thời gian thực.
Nguyên lý cơ bản của quá trình hóa lỏng giúp bạn đạt được sự trộn và truyền nhiệt tốt hơn. Bạn có thể sử dụng quy trình này trong nhiều ngành công nghiệp, như sản xuất hóa chất và sản xuất năng lượng.
Lý thuyết hai pha
Bạn có thể khám phá lý thuyết hai pha để hiểu nguyên tắc cơ bản của sự hóa lỏng sâu hơn. Giả thuyết này cho rằng lớp nền chứa hai pha chính: các hạt rắn và chất lỏng (khí hoặc chất lỏng). Chất lỏng hỗ trợ các hạt bằng cách đẩy chúng lên trên. Các hạt di chuyển và trộn lẫn nhờ lực kéo và lực nổi từ chất lỏng.
Hình học, Các đặc tính vật lý và khí động học của vật liệu rắn dạng hạt đều ảnh hưởng đến sự khởi đầu của quá trình hóa lỏng, và các đặc điểm, hành vi và các thông số chính của tầng sôi. Tính chất rắn quan trọng nhất là: mật độ hạt, bộ xương (ĐÚNG VẬY) Tỉ trọng, mật độ lớn, độ xốp, đường kính hạt tương đương trung bình, hình dạng hạt, phân bố kích thước hạt, và rơi tự do (hoặc thiết bị đầu cuối) vận tốc.
You can see how the two-phase theory developed over time:
Sân khấu | Sự miêu tả | Time Period |
|---|---|---|
1 | Early 1940s | |
2 | Introduction of two phase theory | Early 1950s |
3 | Bubble hydrodynamics studies | Early 1960s |
4 | General understanding of suspension structures | Turn of the century |
The two-phase theory helps you predict how the bed will behave. You can see dense and dilute regions in the bed. The fluid and solid phases interact, which leads to different flow patterns. The table below shows how scientists study these patterns:
Diện mạo | Chi tiết |
|---|---|
Study Focus | |
Điều kiện hoạt động | Superficial gas velocity: 15.5 m/s; Solid flux: 140 kg/m²s; Geldart B particles (sand) |
Những phát hiện chính | Axial solid concentration distribution shows dilute and dense regions. Core-annulus structure and back-mixing near the wall observed. |
Drag Force Model | Revised drag force coefficient based on the EMMS model was proposed and used in CFD simulations. |
Validation Method | Comparison of experimental results with CFD simulations to assess flow structure and pressure drop. |
Phần kết luận | EMMS drag model showed better agreement with experimental data, validating its use in simulations. |
In the two-phase theory, you see the solid phase supported by the fluid phase. The fluidization process depends on how well the fluid can lift and mix the particles. You can use this basic principle to improve chemical reactions and heat transfer in reactors.
Fluidized Bed

How a Fluidized Bed Works
You can see how a fluidized bed operates by watching what happens when you introduce air or liquid from below a bed of solid particles. The upward flow lifts the particles, causing them to move and mix. This movement creates a dynamic system where the particles behave almost like a liquid. You notice different flow regimes as the speed of the fluid changes. The table below shows how the bed changes with each regime:
Flow Regime Type | Sự miêu tả |
|---|---|
Fixed Bed | The initial state where particles are stationary and not fluidized. |
Bubbling Fluidization | Bubbles form within the bed, and particles interact more actively. |
Slugging Fluidization | Large bubbles appear, causing irregular movement of particles. |
Turbulent Fluidization | The flow becomes vigorous, and particles mix rapidly. |
Dilute-Phase Transport | Particles disperse in the gas phase, and concentration drops. |
Fast Fluidization | The bed acts like a fluid, with strong gas and particle interactions. |
Slug/Bubbly Flow | Both slugs and bubbles exist, creating mixed movement. |
Bubble-Free Dense-Phase Flow | The bed stays dense, and gas flow remains low. |
Packed Bed Flow | Particles pack tightly, and fluid movement is minimal. |
bạn có thể suspend solid particles in a continuous liquid phase using gas sparging. The liquid enters from the top and moves against the gas flow. The design of the gas distributor lets liquid exit from the bottom without carrying particles away. This mechanism allows you to use fine or low-density particles in a continuous flow reactor.
Uniform mixing happens when you introduce air from below the powder bed. The air lifts and agitates the particles, turning the dense powder into a fluid-like state. You can spray a liquid binding solution onto the fluidized particles to help granules grow and improve mixing.
Các tính năng chính
You will find several features that make a fluidized bed unique. The table below highlights these important aspects:
Key Feature | Sự miêu tả |
|---|---|
High surface area contact | You get a large contact area between fluid and particles in each bed volume. |
High relative velocities | The fluid and particles move quickly compared to each other. |
Intermixing | Particles mix thoroughly throughout the bed. |
Collisions | Frequent collisions happen between particles and with the walls. |
You need to consider design factors when building a fluidized bed. Particle size distribution affects how much air flow you need. Rounded particles behave differently than oblong ones, which changes drying uniformity. Bulk density influences the minimum velocity needed for fluidization and helps prevent material loss. Specific heat tells you how much energy you need to heat the particles. Fragile particles may need gentle fluidization to avoid breaking. Chemical composition can cause problems like stickiness or heat sensitivity. Inlet air temperature must match what the particles can handle. Air flow velocity controls the fluidization regime and heat transfer. Retention time depends on air flow and weir height, which helps you reach the right moisture level.
Temperature and pressure also affect how the fluidized bed works. Bubble movement controls the flow structure at lower temperatures. At higher temperatures, the way particles stick together becomes more important. Ultra-high temperatures increase interparticle forces, which can change how the particles behave.
Fluidized Bed Reactor
Ứng dụng công nghiệp
You can find fluidized bed reactors in many industries. These reactors help you handle chemical reactions and material processing more efficiently. You see them used in oil refining, chemical production, and energy generation. The design of these reactors lets you mix solids and fluids quickly, which improves the process.
Here are the main types of fluidized bed reactors you might encounter:
Type of Reactor | Sự miêu tả |
|---|---|
BFB (Bubbling Fluidized Bed) | Simple design with a reactor column, distributor, biomass screw feeding system, and cyclone for fine particle removal. |
CFB (Circulating Fluidized Bed) | Consists of a reaction column, multiple cyclones, and a biomass screw feeding system; captures and recirculates coarse and fine particles. |
Entrained Fluid Bed | Uses high gas velocities to keep particles suspended. |
Fluidized bed reactors play a key role in several industrial applications:
Application Type | Sự miêu tả |
|---|---|
Oil and Chemical Processing | Used for continuous feeding and production of bio-oil. |
Synthesis of Acrylonitrile | Employed in the production of acrylonitrile. |
Catalytic Cracking | Utilized in petrochemical industries for catalytic processes. |
Heat Transfer | Efficient heat transfer with uniform bed temperatures. |
You also see these reactors in pharmaceutical manufacturing. They help you dry powders, coat tablets, and mix ingredients. The market for fluidized bed reactors keeps growing. TRONG 2024, the market reached USD 3.5 tỷ. Experts expect it to rise to USD 5.9 tỷ bởi 2033, with a steady growth rate.
Những lợi ích
Fluidized bed reactors offer many advantages for industrial processes. You get better mixing and faster reactions. The design lets you control temperature and material flow easily. You can use these reactors for chemical synthesis, pollution reduction, and material processing.
Benefit/Application | Sự miêu tả |
|---|---|
Chemical Synthesis | Used for synthesizing key plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene, and producing monomers. |
Pollution Reduction | Generates less pollution by using sorbents to capture sulfur and operates at lower temperatures. |
Material and Heat Transfer | Facilitates efficient coating, drying of pharmaceuticals, and quick freezing of food products. |
You notice that heat and mass transfer rates in fluidized beds are much higher than in fixed bed reactors. This makes them ideal for reactions that need efficient heat and mass transfer. You can maintain uniform temperature distribution, which helps with heat transfer. The technology also allows you to regenerate catalysts often without stopping the process.
Fluidized bed reactors help you improve product quality in pharmaceutical manufacturing. You can dry and coat pharmaceutical powders evenly. You also reduce pollution and energy use, which benefits both the environment and your business.
So sánh
Traditional Methods
When you use traditional methods to handle fine solids, you often face many challenges. These methods include free solids splashing, directed gas injection, slugging, and solids entrainment. Each method has its own transport rate and energy efficiency. You can see the differences in the table below:
Phương pháp | Transport Rate (kg/m²·s) | Hiệu quả năng lượng |
|---|---|---|
Free Solids Splashing | 5 × 10⁻²–2 × 10³ | Cao nhất |
Directed Gas Injection | 1.9–4.3 m/s | Intermediate |
Slugging | không áp dụng | Intermediate |
Confined Solids Splashing | không áp dụng | Thấp nhất |
Solids Entrainment | không áp dụng | Thấp nhất |
You may notice that these methods do not always provide high efficiency, especially when you need to control moisture or achieve uniform mixing. Traditional systems often struggle with removing small trash, which can clog pumps and cause scum to build up. Heavy debris can damage equipment, so you need extra screening devices. When you handle high-solids loads, you must use fine screens and grinders to remove debris. These steps lower the overall efficiency and make it hard to control moisture levels.
giới hạn | Impact on Operations |
|---|---|
Causes clogging of pumps and scum accumulation in digesters. | |
Damage from heavy debris | Necessitates additional screening devices to prevent equipment overload. |
Inability to handle high-solids loads | Requires a fine screen coupled with a grinder for effective debris removal in high-solids situations. |
Advantages of Fluidization
When you use fluidization, you gain several advantages over traditional methods. The working principle of fluidization lets you achieve higher efficiency in mixing, truyền nhiệt, and moisture control. You can process a wide range of materials, from grains and spices to chemicals and pharmaceuticals, without changing your equipment. This flexibility means you can dry products with different moisture levels and reach a faster drying time.
Fluidized bed drying adapts to many food products, such as grains, snacks, and spices.
You can use the same equipment in different industries, including pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
The working principle allows you to process materials with various moisture contents, showing great operational flexibility.
You also get better process control and mixing. The working principle of fluidization, especially when combined with vibration, reduces the strong forces between fine particles. This makes it easier to mix and fluidize even the smallest particles. You achieve more even moisture removal and higher efficiency in drying and processing.
Fluidization with vibration breaks up clumps and improves mixing.
You can handle fine particles that are hard to process with traditional methods.
The process gives you more control, leading to better efficiency and more uniform moisture content.
Mẹo: When you need to dry products quickly and evenly, fluidization gives you a faster drying time and helps you reach the desired moisture level with less energy.
You have learned that fluidization turns solid particles into a fluid-like state, which helps you mix, nhiệt, and process materials more efficiently. Fluidized beds and reactors play a key role in many industries. The table below shows some important benefits:
Khu vực ứng dụng | Những lợi ích |
|---|---|
Enhances charging and discharging in solar power plant energy storage systems. | |
Industrial Processes | Increases heat and mass transfer efficiency in various industrial applications. |
High Temperature Energy Storage | Improves power output in sensible and phase-change energy storage systems. |
Research into new fluidization methods, giống Fluidized Bed Fenton technology, can help you treat wastewater better and reduce pollution. You can explore these advances to improve your own work or studies.
Câu hỏi thường gặp
What is fluidization used for in industry?
You use fluidization to improve mixing, sấy khô, và phản ứng hóa học. Many industries rely on this process to boost energy efficiency and product quality. You often see it in food, hóa chất, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
How do you control a fluidized bed?
You control a fluidized bed by adjusting the flow rate of gas or liquid. This lets you manage temperature, trộn, and particle movement. Good control helps you achieve better results and maintain energy efficiency.
Why does fluidization improve energy efficiency?
Fluidization improves energy efficiency because it increases contact between particles and fluids. You get faster heat transfer and better mixing. This means you use less energy to reach the same results.
Can you use fluidization for small particles?
Đúng, you can use fluidization for small particles. You may need special equipment to control the process. This helps you avoid particle loss and maintain stable operation.
What safety tips should you follow with fluidized beds?
You should monitor temperature and pressure closely. Always control the airflow to prevent overheating or blockages. Regular checks keep your system safe and efficient.






